Standards Helping Drive IoT, Smart Grid and Smart Home Technologies
When considering the multitude of connected devices, and the diverse range of broadband wireless access technologies in play with the IoT, Smart Grid and Smart Home technologies, there is a growing need to provide a seamless user experience for applications when a wireless device is performing the handover of IP sessions from one layer 2 access technology to another. To give semiconductor, network equipment, and smart device manufacturers, as well as service providers, a reliable solution, IEEE SA recently released IEEE 802.21—Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks: Media Independent Services Framework and IEEE 802.21.1—Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks: Media Independent Services.
These new standards address the future connectivity and management requirements of Smart Grid, IoT and Smart Home networks, where multimode wireless devices and smart end nodes incorporate different wireless interfaces, and need to switch among them during an ongoing communication session while maintaining the same security posture. For example, during wireless interference, heavy traffic loads, or maintenance on an access point, layer 2 access technology—agnostic secure unicast and multicast-based group communications—with the service provider’s network are essential. When such functionalities and features are invoked, Media Independent Service Function (MISF) comes into play to assist network stacks by exchanging messages among Internet access technologies and the higher layers.
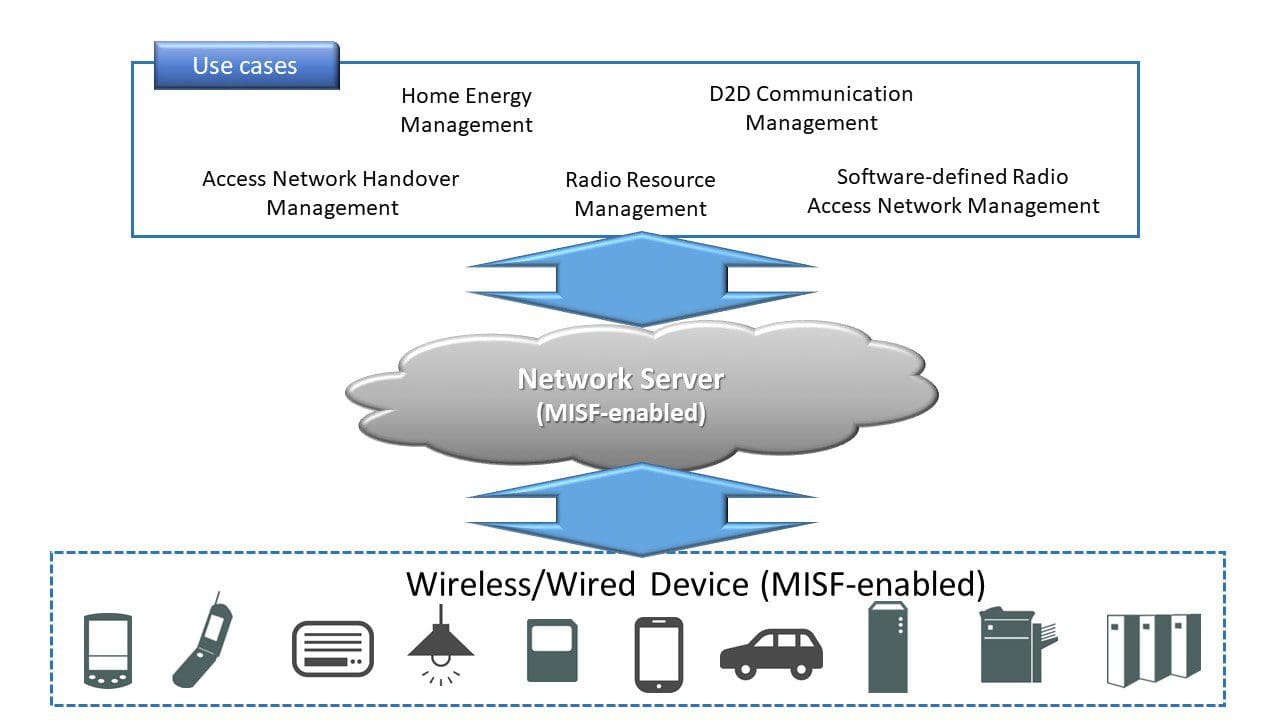
Utilizing IEEE 802.21 framework and IEEE 802.21.1 services, mobile and smart end devices and access points, or gateways, can communicate in a standard way, thus allowing them to make local decisions as to whether and how-to handover a session or join to a multicast group. For core network equipment with no wireless interface, the standard provides for the design of network servers that can make centralized decisions about the handover of sessions among multiple access points and multiple access technologies, and that can manage a group of end points via secure group management capability. This provides a means for wireless network operators and service providers to balance traffic loads, alleviating congestion on specific access points, and delivering on the promise of QoS (Quality of Service) to all users, while maintaining the same security posture managing a group of wireless devices and smart end nodes in Smart Grid, IoT and Smart Home networks
“In step with a desire to advance technology for the benefit of humankind, there are numerous connected device scenarios required to reap the full benefit of robust IoT, Smart Grid and Smart Home technologies,” said Dr. Subir Das, chair, IEEE 802.21 Working Group. “IEEE 802.21 provides a framework that is agnostic to layer 2 access technology and IEEE 802.21.1 addresses several use cases, such as handover between heterogeneous networks, home energy management systems, software-defined radio access networks (SDRANs), radio resource management (RRM), and device-to-device (D2D) communications, and establishes a framework for reliable media independent services that can best meet the needs of a future, greater connected world.”
Learn more about IEEE 802.21, or IEEE 802.21.1.

